How To Properly Use Exposure Compensation Film Cameras
If y'all have a digital camera, the chances are that yous've met a weird-looking scale before. Information technology has numbers from -3 to +3, with a 0 in the middle.
Information technology's the exposure compensation scale.
Today I'll testify y'all how and why it works. Find out how to use exposure bounty to improve your photography workflow.

[ExpertPhotography is supported by readers. Production links on ExpertPhotography are referral links. If you lot use one of these and purchase something nosotros brand a little scrap of money. Need more info?See how information technology all works hither.]


What Is Light?
Allow'southward commencement with at the very basics, at the affair that defines photography: light. You need to understand this in detail to understand exposure. And to understand exposure compensation, you demand to know the concept of exposure.
And so, light travels in waves, like sound. Only, it also has its own substance, photons. It's countable, measurable, and collectable.
Light starts to travel from the light source. It bounces off (reflects) from surfaces, and continues its way in direct lines. It finally ends its journeying at the point where information technology gets fully absorbed.
Light is also a measurable free energy. When something absorbs light, this energy transforms into other forms of energy, similar heat or electricity.
This is why we tin transform information technology into solar free energy. And this is likewise why photography works.
How We Record Lite
When light hits the photographic camera sensor or film, its free energy initiates specific processes. On film, this procedure is a chemical reaction. On digital sensors, the free energy is converted into an electrical current.
More light generates a higher current – less light generates less electricity.

What Is Exposure in Photography?
Exposure is the corporeality of light that a sensor or film detects. Three factors make up one's mind it:
- Scene luminance,which is the intensity of light present in the scene. A bright, sunny twenty-four hour period presents a college scene luminance than a moonlit landscape;
- Shutter speed,which is the length of fourth dimension when the light can pass;
- And Aperture,which is the relative amount of light getting passing through the camera lens.
The above listed three factors determine the full light getting onto the sensor. This is an absolute style of expressing camera exposure, without considering the sensor type and size.
What Is Exposure Value?
Exposure value is the popular way of expressing discontinuity and shutter speed at once. It also reflects the transmission of exposure settings.
These two can be changed in such a way that the total corporeality of light doesn't change. If you double the size of the aperture, you have to half the shutter speed.
If you give with i mitt and have with the other, the total won't change.
In the middle of the 20th century, a simplifying endeavour was launched. It afterward became the Exposure Value System.
The signal is to combine f-finish and shutter speed into ane number: the EV.
This can exist illustrated on an infinite scale of combinations. In the heart, 0 EV is divers equally i 2nd at f/1.
Any other combination resulting in the aforementioned amount of light is as well 0 EV. If you double the shutter speed to ii seconds and decrease the aperture to f/1.4, you'll nonetheless be at 0 EV.
The scale works in doubles and halves. 4 EV is a 2four times higher amount of lite. -four EV is a 24 times lower amount.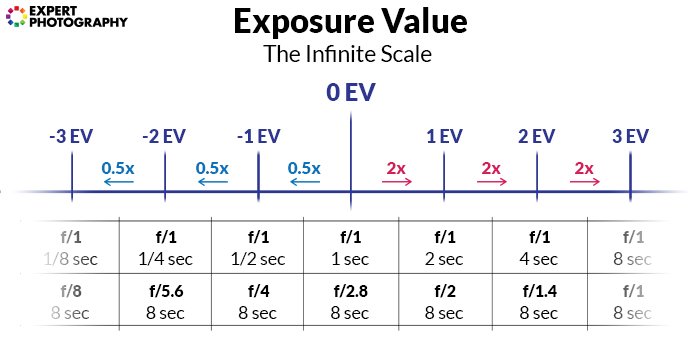
Using ISO to Increase Light Sensitivity
As we discussed, when low-cal hits the sensor, it generates a current.
That electric current is then converted into image information using an counterpart-to-digital (A/D) converter.
However, your image might non look as bright equally you lot'd wish. You tin can find yourself in a situation where your other parameters are fixed. Y'all tin can't play with aperture or shutter speed.
Here comes in ISO. With a higher ISO setting, you can make your sensor more 'sensitive' to low-cal.
Thus, ISO becomes the 3rd parameter thatyoucan control in-photographic camera.
The exposure value scale still works: add ISO 100 everywhere in the previous diagram. You can also increase exposure using only the ISO.
Different discontinuity, ISO is linear. And so 3200 is 32x more than 'sensitive' than 100.
Agreement Dynamic Range
No camera pic or sensor is capable of capturing everything.
A scene contains brighter and darker elements. Brighter things emit or reflect more calorie-free than darker ones.
EVs can also express the luminance differences between these bright and dark things. I'll explain after how.
Dynamic range is the difference between these darkest and brightest parts. This range still contains valuable data.
Contrasty scenes have a wide dynamic range, while misty, mild scenes accept a narrower one. So, a photographic camera sensor will struggle more to capture the contrasty scene.
Midrange digital cameras today have a range of well-nigh x-12 EV. If a scene is less dynamic than this, you have more than room to 'play' with exposure.
If a scene has a wider range than that, you'll either have to cede data or bracket exposures.

Choosing the Right Exposure
What Is the Right Exposure?
Exposure is correct if you, the photographer think it is. Your photographic camera doesn't have an creative vein like you. We need to teach the camera what a correct exposure is. No matter how bright or dark information technology is – if that'southward what you want, it is right.
There is a standard for the algorithmically correct exposure. It's the post-obit:
If an area that is eighteen% grey (eye grey) is exposed to the middle, the exposure is right.
Let me explain.Calibrate Your Photographic camera to Heart Grayness for Correct Exposure
Middle grayness is a shade of grey that our eyes perceive being halfway betwixt blackness and white.
Information technology's not a colour in a scientific sense. It has all the colors in it at the same intensity. So, information technology can be used with both monochrome and color cameras as a reference point.
When you average the luminance levels in a usual scene (say, a cityscape in moderate sunlight), they are very close to the luminance of middle grey.
And so, if nosotros 'teach' our camera that middle grey is a proper exposure, it will too expose correctly in nigh everyday scenes.
Hence, your camera'southward built-in light meter is calibrated to expose for eye greys and anything that has the same luminance.
Yous can purchase grey cards to perfect your own exposures (and colors, besides, to an extent). However, for most applications, it's non necessary.

Measuring the Correct Exposure
Allow'due south photograph a bailiwick with EV 0 settings. And so, for case, at ISO 100, 2 seconds and f/2.
Y'all measure how much brighter or darker the subject is than eighteen% grayness.
With that divergence, you can limited the individual exposure value of a field of study.
And so, if your subject is 8 times darker than middle grey at EV 0 settings, you tin say the luminance of the subject is -3 EV. (Notation: If yous see that a camera can autofocus downwards to -iii EV, information technology's the same matter. Information technology means that it tin accurately catch focus on subjects brighter than -3 EV.)
Your modern camera can also do this for the whole scene.
Measuring Exposure Using Light Metering in Cameras
In erstwhile times, photographers had separate light meters. They would measure exposure by pointing the light meter towards their subjects. They would and then read the measurement, fix the right exposure on the photographic camera, and shoot.
This procedure is what happens is modern cameras too.
Nosotros accept low-cal meters incorporated in the camera bodies. They act equally a very depression-resolution, high-dynamic-range sensor.
The measurement happens after the light has passed through the lens, giving a more authentic result. This is called TTL, Through The Lens metering.
In that location are a few metering modes you can choose from. They use diverse algorithms and preferences that you tin ready.
Metering Modes
These are the modes that almost all mod DSLR and mirrorless cameras have. No matter the brand or price indicate, you'll find these in your camera, too.
- Matrix / Evaluative.This is the most complex one. It meters from the unabridged area of the scene. However, information technology tries to effigy out what's the actual subject and weighs it more than. Ofttimes, it uses focusing distance, colours, tracking and relative size to improve accuracy.
- Centre-weighted Average.A chatty name. Indeed, this way meters the whole scene, weighing the centre parts more than.
- Partial.This way only meters a part of the scene and ignores everything else.
- Spot.Similar to fractional, merely it meters an even smaller, betoken-similar surface area. Old-school lite meters are often spot meters.
When Should You Deviate from the Measured Exposure?
If your photographic camera thinks that everything should exist heart-grey-bright, some things will get wrong.
What'due south the bargain with vivid winter landscapes total of white snow? Or with a nighttime cityscape? In these situations, your camera will probably miss the exposure past default. It will nether and overexpose, in respective social club.
You can besides become into a situation where you take a well-lit subject before a dark background. The chances are that your camera will overexpose because the nighttime groundwork occupies well-nigh of the frame.
But don't requite upwards! Here comes exposure bounty to save you.
What Does the Exposure Compensation Calibration do?
Exposure compensation is a bones setting that you lot can adapt to change the final exposure.
Yous can practise this in semi-automatic modes, and a few cameras accept information technology in manual mode, too.
Where Tin You Discover Exposure Compensation?
You tin can notice the exposure bounty calibration on the main interface of your photographic camera menu. In cameras, it occupies the biggest space in the Q (Quick) menu.


You lot'll also find it on the top LCD screen if yous have one on your camera.

How to Arrange Exposure Compensation
On cameras with two dials, one punch controls the priority setting. The other dial controls compensation.
On cameras with one punch, information technology's a scrap more complicated. For instance, on Canon's lower-range DSLRs, y'all have to printing the compensation button and turn the dial at one time.
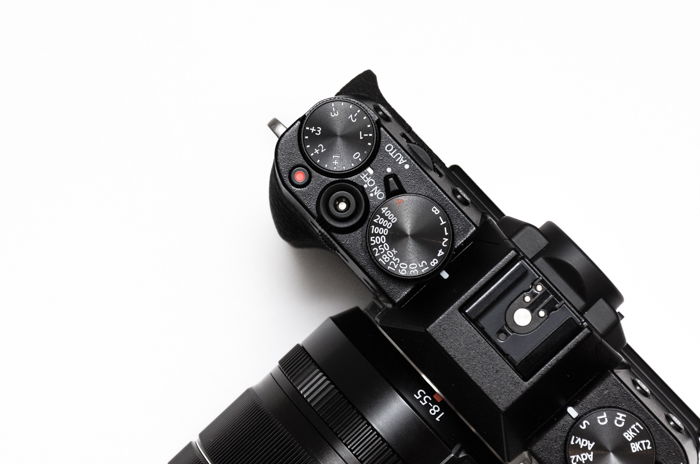


Exposure Compensation in Semi-Automatic Modes
Semi-automated modes are the following:
- P – Programme mode, sets a combination of shutter speed and aperture
- Tv / S – Shutter priority mode, sets the discontinuity automatically
- Av / A– Aperture priority mode, sets the shutter speed automatically
In these modes, the photographic camera measures calorie-free and sets exposure automatically, based on your preferences.
By default, it sets it to the middle. However, you can adjust it to exist darker or lighter. Then, information technology will compensatefor darker or lighter conditions.
Let's go back to our previous example. Suppose y'all have a beautiful, snow-covered landscape earlier you. Your photographic camera is set to Av (aperture priority mode) because you prefer a narrower aperture in the state of affairs.
By default, the camera will assume that the scene is center-grey-vivid. So, it will underexpose it, and indeed, the resulting image will be middle grayness.
Now let's fix the exposure bounty to (around) +1.3 stops. If you have a shot at present, it volition be much closer to the existent luminance of the scene.
You lot can employ it in the dark cityscape state of affairs too.
If you reject exposure compensation by 1-2 stops, your exposure volition give a better representation of the scene.
What Does Exposure Compensation do in Transmission Mode?
Some select cameras, such every bit the Catechism 5D MkIV, have bounty in manual fashion, also.
You can have your aperture and shutter speed fixed. Merely set ISO to Auto, and y'all tin can accommodate the exposure compensation. I discover this to be a practical feature.
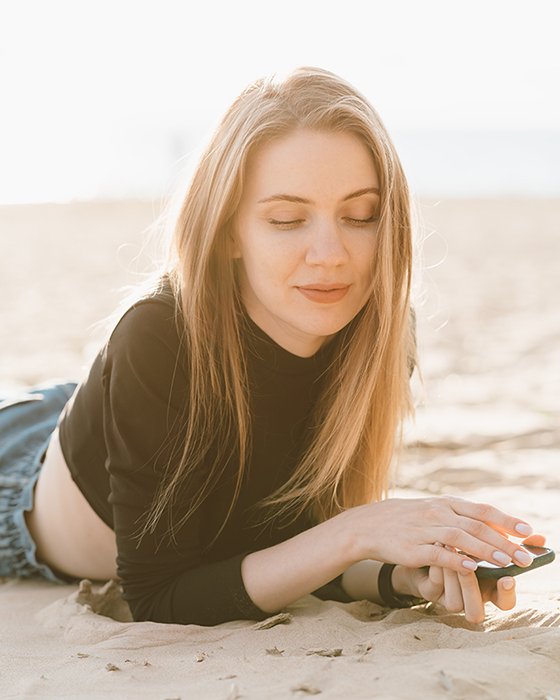

When Should I Adjust Exposure Compensation?
You Demand to Discard Highlight / Shadow Data
In scenes which showroom a wide dynamic range, you have two options. You can shoot more exposures bracketed, and merge them in postal service-production.
Yous tin can merely do this with very steady hands (or a tripod), and where there'due south not much movement in the scene.
Otherwise, you lot'll take to sacrifice either highlight or shadow information and deal with clipping.
However, you surely have preferences on which to go on and which to discard.
In the previous portrait photo, the creative person chose to permit become of some highlight information. In plough, the subject'south face is exposed vivid enough to exist clearly visible (and post-processable).
Set Exposure Compensation for High Cardinal and Low Key Shots
At that place are other, artistic considerations, too. High key and low-primal shots, likewise conscientious lighting, also require over or underexposure (in technical terms).
If you want to photograph in a loftier-central style, yous'll need to gear up exposure compensation to overexpose slightly. Be aware of clipping highlights, though, if that'south non your intention.

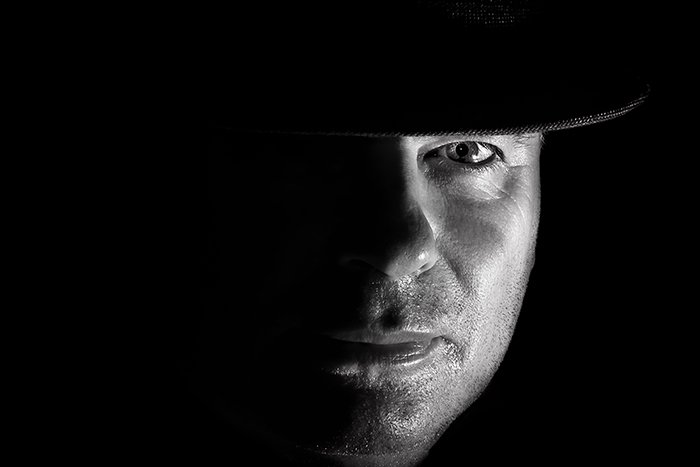
For low-fundamental, you'll need to employ negative bounty, often -iii stops or more. In such scenarios, I recommend using manual way. You can hands manage it with exposure compensation, besides.

Utilise Transmission Mode for Full Control of Exposure
It's worth learning to boom the exposure in transmission mode. Exposure compensation, however practical information technology is, doesn't give yous total control over your camera.
At that place are times when the lighting doesn't let for accurate metering. Concerts, theatres, and nighttime shots, in full general, are hard to accomplish using exposure compensation.
In those situations, you're much meliorate off using transmission, fifty-fifty with limited experience.
Conclusion
Exposure compensation is a powerful feature that allows you lot to eliminate bugging with the settings. It oft gives you more time to concentrate on the bodily photo.
Y'all must know how exposure compensation works, and when and how yous should utilise it.
You should also know the limitations of using exposure compensation. Recognise when it's time to switch to transmission.
Broaden your photography skills with our form: Photography Unlocked!
Source: https://expertphotography.com/exposure-compensation/
Posted by: rollinghend1996.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Properly Use Exposure Compensation Film Cameras"
Post a Comment